Scientific supervisor – G. Tovmasyan
|
In 1989-1991, SKB Granit developed a project for a large orbital telescope of the Schmidt system – ASHOT (Astrophysical Schmidt Orbital Telescope) to solve a wide range of astronomical problems:
This project was international. The ASHOT Observatory was developed in the following cooperation
Work on the project was stopped due to the collapse of the USSR and the reunification of Germany.
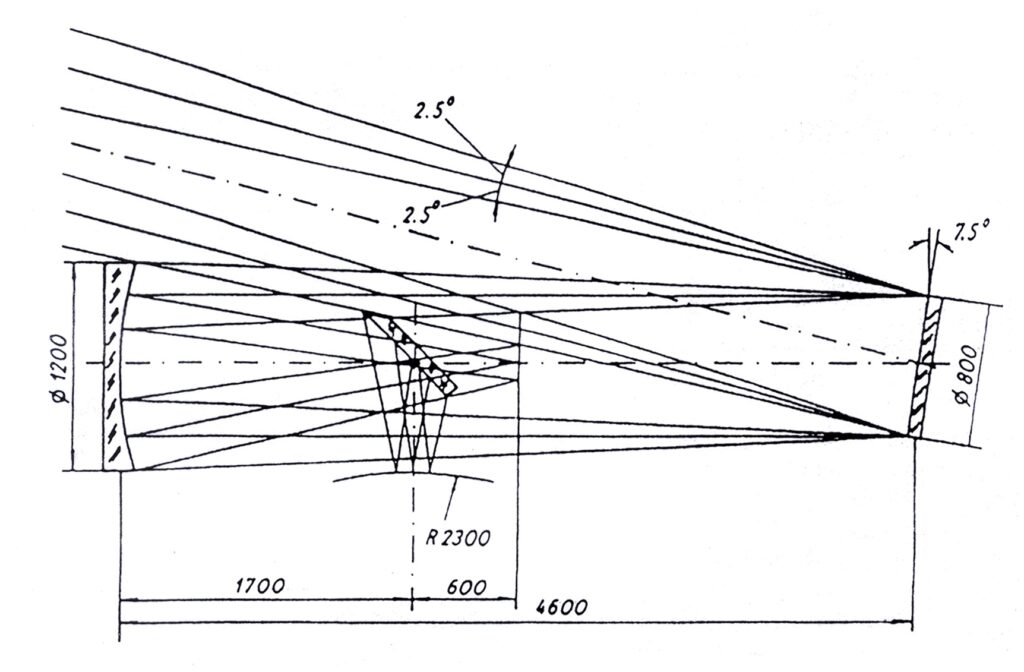
The optical design of the telescope was a Schmidt system with a reflective correction mirror. Basic parameters of the telescope:
The correction mirror is installed in a biaxial suspension, which ensures its rotation for precise guiding. A diagonal mirror is flat, elliptical in shape. Its purpose is to move the focal plane to an area convenient for the location of detectors. Four detectors are installed on a turntable, with the help of which the corresponding detector is installed. This platform has the ability to move along the optical axis within ±1.5mm for focusing. The diagonal mirror is placed in a biaxial suspension with piezo actuators for precise guiding. The telescope has a built-in star sensor for offset guiding. The peripheral part of a telescope’s field of view in which reference stars are selected for guiding, is constructed using a small diagonal mirror located at a distance of 160 mm from the focal surface. The guidance sensor is equipped with a movement mechanism that allows it to be aimed at the selected reference star.
Two options for placing the ASHOT telescope were studied. In one of these options, the telescope was installed in a rotating support device at the MIR orbital station. In the second version, the telescope was placed on a special spacecraft.
Publications:
|
Last Updated on 2024.12.26