Scientific supervisor G. Gurzadyan
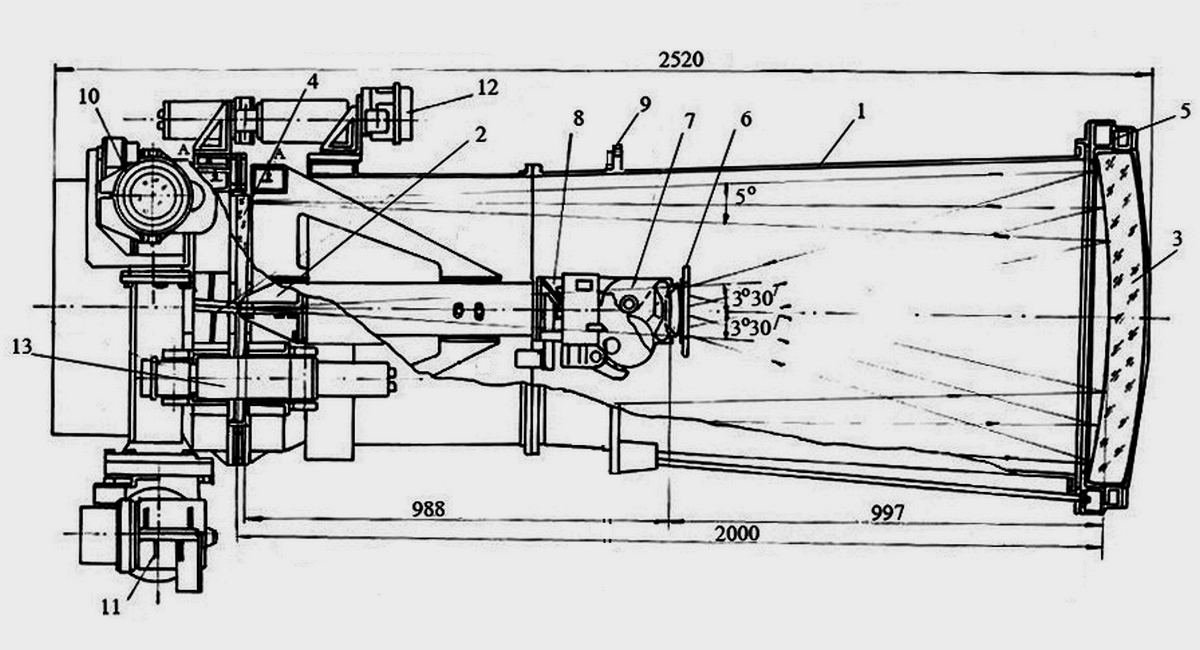
The DRAGON project was developed in 1973-1978 under the leadership of G.A. Gurzadyan to obtain spectral images of the starry sky using a wide-angle 900 mm telescope. An objective prism was located at the telescope entrance as a dispersing element. To ensure high quality shooting, it was installed on a three-axis stabilized platform. In this case, it was planned to use precise KAMERTON star sensors developed at KOMZ within the framework of the PROCION project.
- The goal of the project is spectral images of areas of the sky with a resolution of up to 18 magnitude.
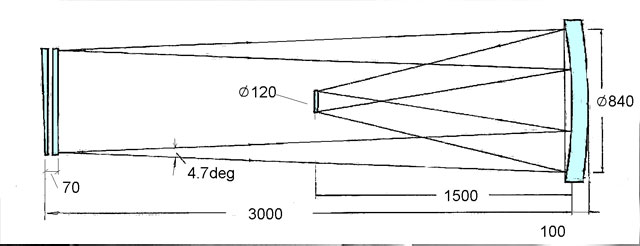
- Telescope – Schmidt system; Main mirror, diameter – 800 mm.
- Image registration is on UV photographic film.
- Stabilization by two reference stars by rotating a bunch of star sensors and a photo cassette relative to the center of curvature of the main mirror.
- Three-axis gimbal – on elastic hinges with precision wave gears and a ball screw mechanism.
- Tracking accuracy ± 2″.
Basic parameters of the optical design
| Optical design Schmidt Spectral range 800-3800 A Inlet diameter 600 mm Focal length 1500 mm Relative aperture 1:2.5 Field of view 4.7 degrees Image diameter, mm 120 |
Main mirror diameter 900 mm Prism angle 2 degrees Linear dispersion, A/mm at wavelength – 1900 A 120 – 2500 A 330 – 3000 A 650 |
 |
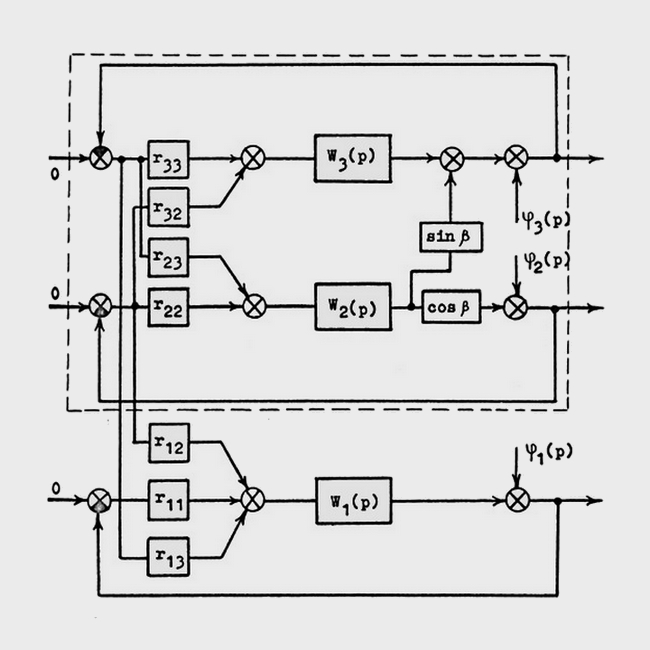 |
| Design of the DRAGON telescope | Block diagram of the DRAGON telescope stabilization system |
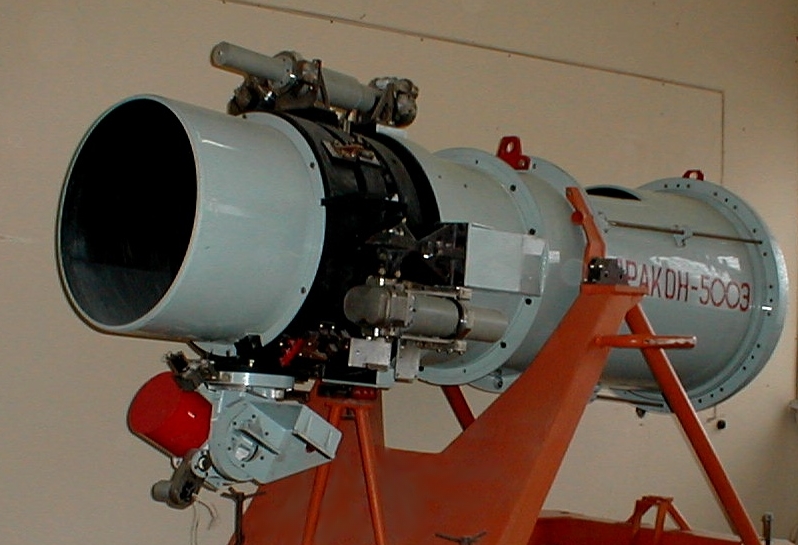
It was assumed that a specialized automatic satellite would be created on the basis of the SOYUZ spacecraft, conducting the experiment in autonomous mode and docking with a manned orbital station only to replace photo cassettes or to carry out repair and maintenance work. At the preliminary design stage, a working prototype was developed and manufactured in Garni, albeit in a version with a 500 mm mirror. Unfortunately, for a number of reasons, including financial reasons, the work was suspended and then closed altogether.

Last Updated on 2025.01.10