The following works were performed in cooperation with SKB Granit for organizations of the USSR Academy of Sciences:
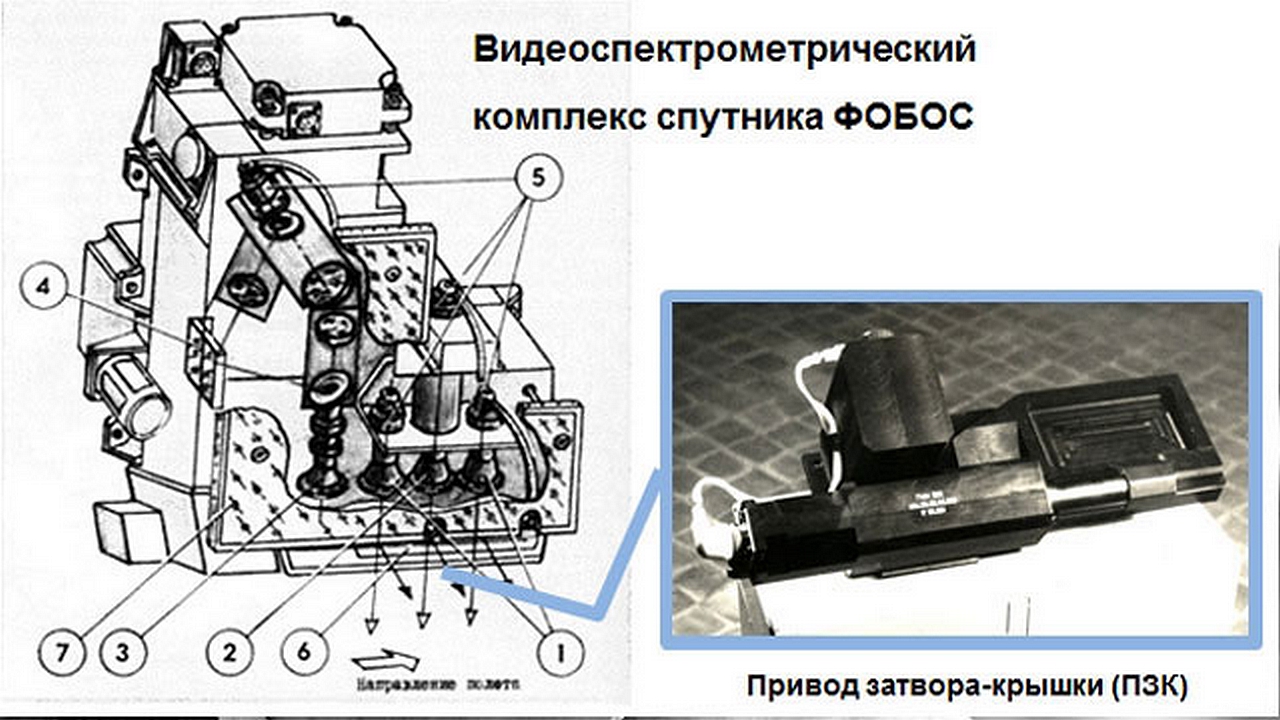
PZK (Phobos) To implement the tasks of spectrometry of Phobos and Mars, scientists from the Soviet Union, Bulgaria and the GDR jointly developed a complex that included two wide-angle and one narrow-angle cameras, a spectrometer and a video storage device. CCD matrices were used as radiation receivers in the television cameras and spectrometer. Wide-angle cameras provide two-zone imaging of Phobos with a large coverage area, which is necessary for compiling topographic, geological and morphometric maps.
The narrow-angle camera made it possible to obtain images with high spatial resolution, necessary for studying the small-scale structure of the surface of Phobos and was intended to solve navigation problems; detailed survey of the hovering area from synchronous orbit, as well as survey of Mars. At the entrance of the television cameras, a mirror-cover (PZK) was located, which in the closed position protected the lenses and made it possible to carry out end-to-end photometric calibration of the television cameras from internal radiation sources, and in the open position – the planned survey of Phobos. In two intermediate positions, the optical axes of television cameras were rotated by 75.5 degrees – for panoramic photography of Phobos and by 87 degrees – for shooting Mars and navigation senses. The TEREK telescope consisted of three blocks: a database sensor block and two electronics blocks. The database included three measuring channels for recording images of the Sun and its corona in three different X-ray wavelength ranges. During the TEREK experiment, conducted on board the Phobos-1 interplanetary station in 1988. For the first time, using the technology of multilayer X-ray optics and detectors based on CCDs and image intensifiers, long-term studies of short-wavelength (VUV) radiation from the Sun were carried out using the method of imaging spectroscopy, as a result of which 150 images of the Sun were obtained in the ranges of 17.5 nm (FeIX-XI lines) and 30.4 nm (HeII line) with an angular resolution of 10-15″ over a period of about 1 solar revolution.
Publications:
|
Last Updated on 2024.12.25